Publications
Insights and Analysis: This collection offers in-depth analysis and findings from leading studies, highlighting the current state of AI development, opportunities, and challenges across the continent. These resources provide valuable information for understanding trends, strategies, and the impact of AI on various sectors in Africa.

Africa AI Privacy Report 2025
Examines AI's transformation of Africa's digital landscape across finance, healthcare, law enforcement, education, and governance. Analyzes privacy challenges, regulatory gaps, and offers strategic policy recommendations to balance technological advancement with fundamental rights protection.

Adopting AI in Africa’s Judicial Systems
AI is transforming global judicial systems. In Africa, it offers solutions to backlogs and inefficiencies but must be tailored to local contexts, with ethical safeguards and inclusive implementation.
Policy Guidelines For The Integration of Artificial Intelligence in African Judicial Systems
African judicial systems face challenges like backlogs, language barriers, and limited resources. AI offers solutions—faster research, judgment writing, and access to legal info—but raises ethical concerns. A cautious, rights-based, continental approach can promote responsible AI adoption through shared standards, mutual learning, and contextual innovation.
Leveraging AI-Powered Mechanisms to Improve Small Claims Courts in Africa
Small Claims Courts offer fast, affordable justice for minor disputes, easing burdens on traditional courts. Despite benefits, challenges persist—AI can help improve efficiency, access, and legal innovation.

Bridging the Justice Gap: Artificial Intelligence as a Tool for Judicial Efficiency in African Countries
Judicial systems in African countries face a myriad of challenges- ranging from poor record keeping and case management, to insufficient staff and resources. The system also heavily relies on human capacity for daily operations, including the filing of court cases, manual writing of court proceedings, documentation, and record keeping. All together, these challenges result in case delays, high case backlog, which not only erodes trust in judicial systems but also limits the efficient administration of justice. This policy brief examines the challenges facing the judicial systems of various African countries, and explores how Artificial Intelligence (AI) models can be deployed to solve these challenges

5 Years of AI Regulation in Africa
AI is transformative but faces challenges in Africa, including policy gaps, infrastructure issues, and the need for local talent.

AI & the Future of Judicial Systems in Africa 2024
The report analyzes AI's transformative impact on Africa's judicial systems, highlighting adoption challenges, benefits, and governance strategies.

Learning Note: Introduction to a data and analytics strategy
Many organizations lack a clear digital transformation strategy, making data strategy development crucial for Rwanda’s Economy Digitalization Programme. This initiative helps institutions maximize data assets and drive growth. A comprehensive data strategy was tested across Rwanda's public institutions, focusing on aligning data use with organizational goals for improved decision-making.

From the margins to the center: Africa's role in shaping AI governance
Africa has the potential to transition from an AI consumer to a developer by addressing infrastructure gaps, fostering talent, enhancing data ecosystems, and promoting regional collaboration. Inclusive AI governance and sufficient funding are essential to ensure equitable benefits and active African participation in shaping global AI efforts.

6 ways Google is working with AI in Africa
Google's AI center in Accra tackles global challenges, including flood forecasting, locust prediction, maternal health, and literacy improvement.

Landscape study of AI policies and use in Southern Africa
AI has the potential to support inclusive economies in Africa, but its proliferation poses risks that may worsen social and economic inequalities. A study assesses AI use and regulatory frameworks in Southern Africa, aiming to promote ethical governance and highlight opportunities across sectors like healthcare, education, and labor.

A New Dawn: Embracing Ethical Adoption And Adaptation Of Artificial Intelligence (AI) In Africa
AI is driving transformative advancements across Africa, revolutionizing sectors like healthcare, agriculture, and education, while addressing key challenges.

AI and the Future of Work in Africa White Paper
The white paper discusses the implications of Generative AI on Africa's future of work, emphasizing inclusive policies, human-centered design, local solutions, and investment in infrastructure and education.

Deloitte's latest report on "AI for Inclusive Development in Africa
Africa's AI potential is hindered by data scarcity, limited infrastructure, and the digital divide. Despite efforts to bridge this gap, significant investments in digital infrastructure and AI-specific tools are needed to unlock AI's benefits for the continent.

From the margins to the center: Africa's role in shaping AI governance blog article published by World Bank
Africa has the potential to become a major AI player but faces challenges. To realize this, inclusive AI governance is crucial, considering Africa's unique context and priorities. Significant investments and policy frameworks are needed to harness AI's benefits and avoid potential risks.
Protection of Personal Information Framework South Africa published
The Protection of Personal Information Act (POPIA) in South Africa requires researchers, institutions, and investigators to comply with data privacy regulations. This framework provides guidelines to ensure research projects adhere to POPIA, protecting personal information and establishing data security measures.

New research, “AI and the Global South: The Role of Civil Society in AI Decision-Making’(CARE INTL UK)
This report highlights the role of Global South civil society organizations (CSOs) in AI governance. It explores their insights on effective AI inclusion and decision-making processes, aiming to inform future AI development and policy.

Detecting Cervical Cancer Through Artificial Intelligence Powered Digital Microscopes In Africa
AI technologies like PapsAI are enhancing cervical cancer diagnosis and treatment in Africa, improving early detection and reducing mortality.

Harnessing power of language, tech to boost SME digital trade
Africa's MSME sector, powered by local languages and informal trade, drives 80% of the continent's commerce. Incorporating African languages into digital tools can enhance e-commerce, empower youth and women, and bridge global digital divides.

Pact for the Future
The Pact for the Future emphasizes global cooperation to address transformative challenges like climate change, inequality, and poverty, aiming for a sustainable, inclusive, and just future. It reaffirms commitments to international law, human rights, sustainable development, and gender equality, advocating for multilateralism and collective action. The Pact includes 58 actions for progress across development, peace, technology, and global governance, with a review set for the 83rd UN General Assembly session.

Can AI improve health care delivery in Africa? 5 things you should know
The potential of AI in African health care hinges on localization, infrastructure investment, oversight, cost-effectiveness, and empowering local innovators to address biases and create inclusive, impactful solutions.

AI in Africa
Africa is central to the global AI supply chain but faces challenges with foreign tech dominance. Local strategies should focus on inclusive development and gender equality.

Governing AI in Africa: Policy frameworks for a new frontier
AI will revolutionize Africa, driving sustainable growth, innovation, and opportunity across sectors like business, health, and agriculture.

Voice and Access in AI: Global AI Majority Participation in Artificial Intelligence Development and Governance
AI's transformative potential is hindered by unequal access, excluding the Global AI Majority. This paper proposes remedies like infrastructure development, education, participatory governance, and safety mechanisms to ensure equitable benefits.

Governing AI for Humanity
Artificial intelligence (AI) offers vast potential to advance scientific inquiry, public health, and sustainable development. However, AI governance is essential to address risks like bias, disinformation, and inequitable benefits. Current regulatory systems are fragmented, lacking accountability and clear standards.
Can AI help Africa close the development gap?
AI is transforming Africa with solutions in healthcare, education, and agriculture, while raising concerns about inequality, data privacy, and dependency on foreign tech giants.

Case studies of AI policy development in Africa
Artificial intelligence (AI) requires new ways of evaluating national technology use and strategy for African nations. We conduct a survey of existing “readiness” assessments both for general digital adoption and AI policy in particular. We conclude that existing global readiness assessments do not fully capture African states’ progress in AI readiness and lay the groundwork for how assessments can be better used for the African context. We consider the extent to which these indicators map to the African context and what these indicators miss in capturing African states’ on-the-ground work in meeting AI capability. Through case studies of four African nations of diverse geographic and economic dimensions, we identify nuances missed by global assessments and offer high-level policy considerations for how states can best improve their AI readiness standards and prepare their societies to capture the benefits of AI.
Artificial Intelligence in Sub-Saharan Africa: Ensuring Inclusivity
AI is disrupting global development sectors, offering benefits but facing slow adoption and infrastructure challenges in Africa. Inclusivity in AI policies and infrastructure is crucial for equitable progress.

Ethical Governance of AI in the Global South: A Human Rights Approach to Responsible Use of AI
AI's transformative potential is vast, with applications in various fields. However, the global south faces risks due to governance gaps and exploitation by developed nations, including resource extraction and invisible labor. Ethical governance is crucial to address these disparities.

AI from the Global Majority Report
The 2024 DAIG Coalition report highlights inclusive AI governance, focusing on the Global South's experiences, challenges, and contributions to equitable, rights-based, and sustainable frameworks.

AI for Africa: Artificial Intelligence for Africa's Socio-Economic Development by African Union Development Agency (AUDA-NEPAD)
The report outlines AI's potential to boost Africa's growth in key sectors but notes challenges in infrastructure and policy.

Unpacking the potential of Artificial Intelligence to accelerate youth development in Africa.
AI has transformative potential for youth development in Africa, addressing key sectors like healthcare, education, and governance. The AU’s AI Continental Strategy and upcoming policy brief emphasize AI’s role in industrialization, job creation, and sustainable development, aligning with Agenda 2063 goals.

AU AI Continental Strategy Analysis
The AU's 2024 AI Strategy, emphasizing inclusive governance, aims to address AI benefits and risks, promote data-sharing, harmonize regulations, and ensure ethical AI use aligned with Africa's development priorities.

Kenya to restrict use of locals’ data for foreign AI training
Kenya plans to restrict foreign use of citizens’ data for AI training, emphasizing data sovereignty, robust governance, local storage, and international advocacy for ethical AI regulations.

AI for Africa: Use cases delivering impact
AI has potential to drive Africa's development and SDGs, but challenges include limited local data, infrastructure, and skills.
AI has an environmental problem. Here’s what the world can do about that.
AI has the potential to address environmental crises but also contributes to issues like electronic waste, water consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions from data centers. UNEP urges sustainable AI deployment by improving regulations, efficiency, and renewable energy use in data centers.

New Deal Technologique: Horizon 2034
Senegal launched the #NewDealTechnologique to become a digital services leader by 2034, leveraging AI to drive digital sovereignty, public service digitalization, economic growth, and African digital leadership.

A vision for public AI in Africa
Imagine a world where AI isn’t just a tool for tech giants to amass more power but a collaborative force that uplifts entire communities. Now, picture this world taking shape in Africa, where the constraints of limited resources are turning into catalysts for ingenious solutions. This isn’t a far-fetched dream—it’s a vision of sustainable and collaborative AI innovation that might be the key to transformation across the continent.

The Bletchley Declaration by Countries Attending the AI Safety Summit, 1-2 November 2023
AI offers significant global opportunities but also poses substantial risks, especially in areas like cybersecurity and disinformation. International cooperation is essential to ensure safe, human-centric, and responsible AI development, with a focus on ethics, transparency, and equitable distribution of benefits.

The Paradox of Africa's Autonomy in Shaping its AI Future
Africa has made strides in AI, but progress is limited and heavily influenced by external actors, unlike other global regions investing billions to lead and govern AI innovation independently.

Artificial Intelligence Revolution in Africa: Economic Opportunities and Legal Challenges
AI is growing rapidly and impacting daily life, but its adoption in Africa faces challenges affecting economic development.
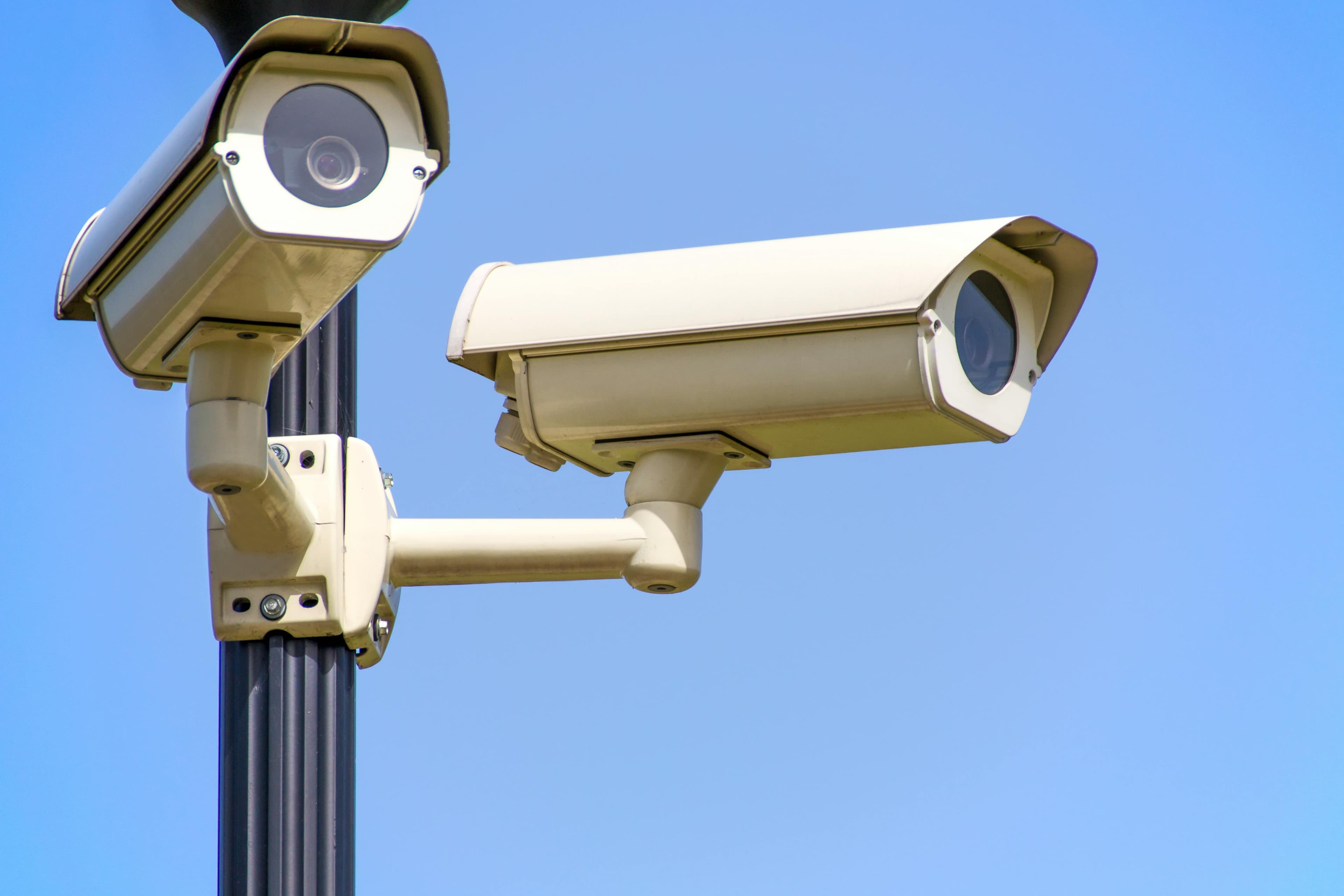

Red Lines for AI: Restricting surveillance, reclaiming privacy
AI surveillance technologies are used by 75 out of 176 countries, affecting over 6.9 billion people. The lack of strong global regulations allows widespread surveillance, posing privacy risks. The European Parliament's AI Act aims for regulation but doesn't fully ban certain rights-infringing uses. ARTICLE 19 advocates for stricter regulations and clear boundaries to protect human rights and privacy.

Artificial Intelligence (AI) Deployments in Africa: Benefits, Challenges and Policy Dimensions
Africa lacks comprehensive AI data and faces challenges in policy, equity, and inclusion to harness AI benefits effectively.

AI and the Global South: The Role of Civil Society in AI Decision-Making
AI's rapid growth risks excluding Global South communities from governance. New CARE International research highlights four pathways for inclusive AI: literacy, local representation, advocacy, and equitable data governance.

AI for Inclusive Development in Africa Part 2: Data and Digital Infrastructure
African countries face significant challenges in AI adoption due to data deficits, limited infrastructure, and uneven internet connectivity. Bridging the digital divide, improving data security, and investing in AI-specific infrastructure like high-performance data centers and GPUs are essential to harness AI's potential for socio-economic advancement.
How to win with AI
The ability to power each machine individually allowed manufacturers to reorganise factories. Because energy needs no longer constrained where machines were located, manufacturers could arrange machines so that materials moved linearly through the factory without having to backtrack to previous stages of production. Electricity also made it easier to operate a subset of machines, making it more convenient to operate multiple shifts or shut down part of the factory for repairs or adjustments.

AI policy Blueprint for Africa
The guidelines aim to help Canadian judges navigate AI use in courts, balancing innovation with caution. They emphasize awareness, caution, and leadership to ensure judicial independence, fairness, and access to justice.

Can Africa Accelerate A Post COVID-19 Socio-Economic Transformation Through Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Technologies?
AI-enabled technologies can drive Africa’s socio-economic development, offering solutions in health, finance, agriculture, and more, especially post-pandemic.

Africa and The Reform of The Multilateral System: The Summit of The Future and Beyond
Report of the Joint Namibia-Amani Africa High-Level Panel of Experts on Africa and the Reform of the Multilateral System in a changing Global order

AI Is Here to Stay! How Artificial Intelligence Can Contribute to Economic Growth in Africa
AI can drive Africa's development by enhancing healthcare, education, agriculture, and addressing sustainability, despite challenges.
Artificial Intelligence for Development (Quarter 2 2024)
AI and machine learning offer transformative potential for economic growth and sustainable development in Africa. However, challenges like algorithmic bias persist. Africa Development Insights explores how UNDP and partners can maximize AI's benefits while minimizing risks for African economies.

The Role of AI Innovation Clusters in Fostering Youth Employment in Africa
AI innovation clusters in South Africa, Egypt, Nigeria, and Kenya drive economic growth and job creation. This report highlights challenges, explores grassroots AI communities, and offers recommendations for strengthening clusters to boost youth employment and economic development.

Artificial Intelligence in Africa: Emerging Challenges
AI ethics discussions often neglect Africa, but the continent is innovating and needs inclusive, culturally aware approaches to AI.

Africa Now Has a Continental AI Strategy: What Next?
AI development in Africa is advancing, with benefits in healthcare, agriculture, and social services, but also posing unique risks. The AU’s AI Strategy, supported by UNESCO and experts, emphasizes ethics, inclusion, and equitable AI governance to align with African values and development goals.

Coming to Life: Artificial Intelligence in Africa
AI investment surged globally in 2016, but its adoption in Africa is limited due to infrastructure and policy challenges.

A new technology Cold War: How Africa can navigate the latest US export controls on AI
The U.S. has imposed sweeping export controls on AI and advanced technologies, targeting adversaries like China. African nations, categorized under Tier 2, face challenges and opportunities to strengthen self-reliance, regional alliances, and local innovation amidst widening technology gaps.

Artificial Intelligence. African Insight.
A collaborative project supports African research on AI ethics and human rights, addressing local challenges and opportunities.
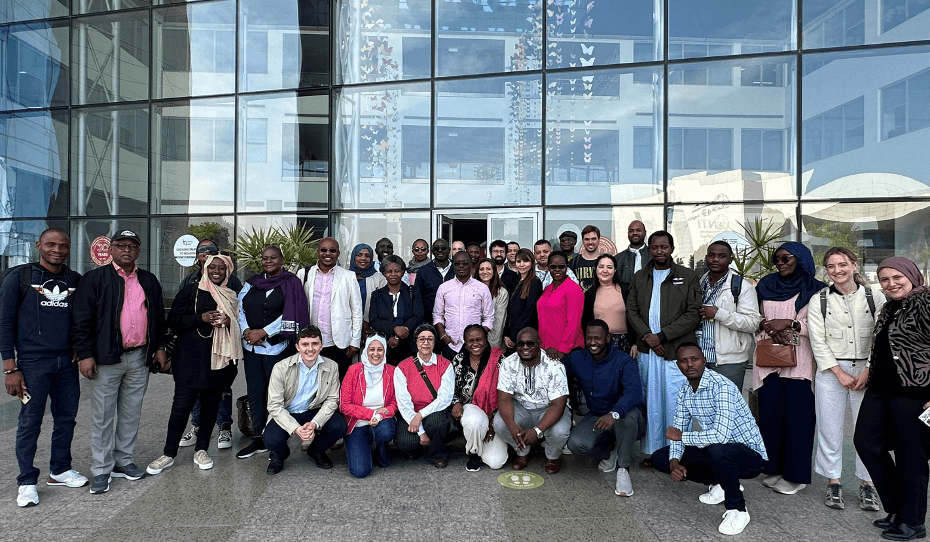
The OECD-African Union AI Dialogue 2.0: From strategy to implementation
The OECD-AU AI Dialogue in Cairo united 30+ countries to advance Africa’s Continental AI Strategy, emphasizing regional collaboration, diverse contexts, capacity building, and trust in AI governance.

The State of AI in Africa
Africa's AI adoption is growing, with significant potential but facing challenges in data access, education, and policy frameworks.
Do we need a ministry of Artificial Intelligence in Uganda? Building a future that belongs to us
There is growing debate on Uganda's AI readiness and whether a Ministry of AI is necessary. Uganda ranks low globally but has potential by addressing key gaps in strategy, infrastructure, and talent development.
Beyond the good and bad: Making sense of the AU-Continental AI Strategy for African people
The African Union has endorsed a strategy to harness AI for Africa's development. This move is seen as a significant step towards Africa's participation in the global AI conversation. While the strategy presents a hopeful vision for Africa's future, Pollicy calls for a more nuanced approach that centers the needs of the common African. This approach will ensure that AI is used ethically and responsibly to benefit all Africans.

AI Governance in Africa Report 2022
AI shows promise for Africa but also poses risks. Governance is slow, with gaps in legislation and human resources.

Artificial intelligence in Africa: challenges and opportunities
AI's transformative potential across industries is driving global attention. In Africa, AI's impact and opportunities are still emerging, with significant regional development.
Beyond the good and bad: Making sense of the AU-Continental AI Strategy for African people
The African Union endorsed its AI strategy, emphasizing development, prosperity, and Africa's active role in global AI. Critiques include limited public involvement, feasibility concerns, and foreign influence risks.

AI for the Global Majority: The Digital Divide No One’s Talking About!
The glossy and rapid expansion of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and its promise of transforming every aspect of our lives is tarnished by a growing undercurrent of exclusion. This blog authored by GDIP’s digital inclusion advocate and policy expert Onica Nonhlanhla Makwakwa explores some of the most significant barriers to digital inclusion in the age of hashtag#AI. Delve in to learn key insights from our roadmap for inclusive AI development as we detail the importance of ensuring AI’s potential is underpinned by hashtag#digitalinclusion principles

5 essential API design patterns for successful model implementation
📊 Did you know 70-85% of AI implementations fail to deliver the expected ROI? The culprit is often poor API design! Check out my latest article where I break down 5 essential API design patterns that can help your AI projects succeed where others fail: ✅ RESTful Resource Modeling ✅ Asynchronous Processing with Webhooks ✅ Consistent Error Handling ✅ Versioning Strategy ✅ Authentication & Rate Limiting Real code examples included! hashtag#AIImplementation hashtag#APIDesign

AI in Africa Meeting the Opportunity
AI has transformative potential for Africa, promising economic growth and innovation if harnessed responsibly and inclusively.

Facilitating agency in Ghana’s tech ecosystem: Lessons from Mazzuma and Ghana NLP
Multinational corporations dominate AI in Africa, amplifying inequities from digital divides. Ghana’s Mazzuma and Ghana NLP counter this by promoting locally tailored, open-source, and community-driven AI solutions.

Shaping the future of AI in Africa
The brief urges Africa to shape its AI future through collaboration, innovation, and ethical development, addressing infrastructure and policy gaps to harness AI for inclusive, sustainable growth.

AI for Africa by Africa: the revolution must be led not bought
The world’s attention is increasingly shifting to Africa, with global tech leaders recognizing the continent’s explosive growth potential. Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, has echoed a sentiment that is now gaining traction among global investors: "Africa is going to be the fastest growing and most important market over the next coming decades." However, while Africa’s market potential is undeniable, the real conversation should focus on ownership, innovation, and value creation within the continent.

Africa Sandboxes Outlook: Thinking outside the box for responsible innovation in the age of AI
Sandboxes are emerging as useful tools for testing regulatory and technical innovations capable of tackling the complex challenges presented by data and artificial intelligence (AI). Their potential is being explored in Africa to support data governance innovation and support data value creation. As part of the Datasphere Initiative’s Africa Sandboxes Forum, this report presents research and analysis of current sandbox experiences in Africa and offers recommendations for supporting their use to tackle complex regulatory challenges.
Why Global South Countries Need to Care About Highly Capable AI
Highly capable AI, primarily developed in Global North countries, could disproportionately impact Global South vulnerabilities, risking catastrophic outcomes. Stakeholders must act to ensure equitable, transformative AI development globally.
The synergy of AI & Sustainability
This is Article is more tailor made to show why the World should watch out for Africa in the AI race. They should watch-out. From AI-optimized renewable energy grids to intelligent climate modeling, explore the innovations driving us toward a greener, more efficient future.

Against All Odds: Increasing African Women's Influence on AI Innovation and Policy
Africa is becoming an AI innovation hub, with women playing key roles despite challenges. Advocates like Linda Bonyo emphasize capacity-building, gender equity, inclusive governance, and funding support to empower African women in AI.

Artificial intelligence needs assessment survey in Africa
UNESCO supports AI development in Africa, focusing on education, ethics, gender equality, and sustainable socio-economic growth.
OECD – FSB Roundtable on Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Finance1
The OECD-FSB Roundtable discussed AI's rapid adoption in finance, focusing on its benefits in efficiency, fraud detection, and customer service, while highlighting concerns like data protection, governance, and potential financial stability risks. It emphasized the need for risk-based management, international cooperation, and regulatory oversight for safe AI deployment in financial services.

The Global South needs to own its AI revolution
On the current trajectory, the Global North will continue to dominate AI and develop new forms of economic and cultural dependency. But with investment in distributed computing and grassroots innovation, low- and middle-income countries can establish a fairer technological order that creates value for their communities.

The USA White House publishes its first ever National Security Memorandum on AI
The US government aims to leverage AI for national security, but it must be used responsibly, ethically, and in compliance with laws and international norms.

Africa AI Privacy Report 2025
Examines AI's transformation of Africa's digital landscape across finance, healthcare, law enforcement, education, and governance. Analyzes privacy challenges, regulatory gaps, and offers strategic policy recommendations to balance technological advancement with fundamental rights protection.

Adopting AI in Africa’s Judicial Systems
AI is transforming global judicial systems. In Africa, it offers solutions to backlogs and inefficiencies but must be tailored to local contexts, with ethical safeguards and inclusive implementation.

5 Years of AI Regulation in Africa
AI is transformative but faces challenges in Africa, including policy gaps, infrastructure issues, and the need for local talent.

AI & the Future of Judicial Systems in Africa 2024
The report analyzes AI's transformative impact on Africa's judicial systems, highlighting adoption challenges, benefits, and governance strategies.

Deloitte's latest report on "AI for Inclusive Development in Africa
Africa's AI potential is hindered by data scarcity, limited infrastructure, and the digital divide. Despite efforts to bridge this gap, significant investments in digital infrastructure and AI-specific tools are needed to unlock AI's benefits for the continent.

Pact for the Future
The Pact for the Future emphasizes global cooperation to address transformative challenges like climate change, inequality, and poverty, aiming for a sustainable, inclusive, and just future. It reaffirms commitments to international law, human rights, sustainable development, and gender equality, advocating for multilateralism and collective action. The Pact includes 58 actions for progress across development, peace, technology, and global governance, with a review set for the 83rd UN General Assembly session.

AI in Africa
Africa is central to the global AI supply chain but faces challenges with foreign tech dominance. Local strategies should focus on inclusive development and gender equality.

Governing AI for Humanity
Artificial intelligence (AI) offers vast potential to advance scientific inquiry, public health, and sustainable development. However, AI governance is essential to address risks like bias, disinformation, and inequitable benefits. Current regulatory systems are fragmented, lacking accountability and clear standards.

Artificial Intelligence in Sub-Saharan Africa: Ensuring Inclusivity
AI is disrupting global development sectors, offering benefits but facing slow adoption and infrastructure challenges in Africa. Inclusivity in AI policies and infrastructure is crucial for equitable progress.

AI from the Global Majority Report
The 2024 DAIG Coalition report highlights inclusive AI governance, focusing on the Global South's experiences, challenges, and contributions to equitable, rights-based, and sustainable frameworks.

AI for Africa: Artificial Intelligence for Africa's Socio-Economic Development by African Union Development Agency (AUDA-NEPAD)
The report outlines AI's potential to boost Africa's growth in key sectors but notes challenges in infrastructure and policy.

AI for Africa: Use cases delivering impact
AI has potential to drive Africa's development and SDGs, but challenges include limited local data, infrastructure, and skills.

Red Lines for AI: Restricting surveillance, reclaiming privacy
AI surveillance technologies are used by 75 out of 176 countries, affecting over 6.9 billion people. The lack of strong global regulations allows widespread surveillance, posing privacy risks. The European Parliament's AI Act aims for regulation but doesn't fully ban certain rights-infringing uses. ARTICLE 19 advocates for stricter regulations and clear boundaries to protect human rights and privacy.

Artificial Intelligence (AI) Deployments in Africa: Benefits, Challenges and Policy Dimensions
Africa lacks comprehensive AI data and faces challenges in policy, equity, and inclusion to harness AI benefits effectively.

AI for Inclusive Development in Africa Part 2: Data and Digital Infrastructure
African countries face significant challenges in AI adoption due to data deficits, limited infrastructure, and uneven internet connectivity. Bridging the digital divide, improving data security, and investing in AI-specific infrastructure like high-performance data centers and GPUs are essential to harness AI's potential for socio-economic advancement.

Africa and The Reform of The Multilateral System: The Summit of The Future and Beyond
Report of the Joint Namibia-Amani Africa High-Level Panel of Experts on Africa and the Reform of the Multilateral System in a changing Global order

Artificial Intelligence for Development (Quarter 2 2024)
AI and machine learning offer transformative potential for economic growth and sustainable development in Africa. However, challenges like algorithmic bias persist. Africa Development Insights explores how UNDP and partners can maximize AI's benefits while minimizing risks for African economies.

The Role of AI Innovation Clusters in Fostering Youth Employment in Africa
AI innovation clusters in South Africa, Egypt, Nigeria, and Kenya drive economic growth and job creation. This report highlights challenges, explores grassroots AI communities, and offers recommendations for strengthening clusters to boost youth employment and economic development.

Artificial Intelligence in Africa: Emerging Challenges
AI ethics discussions often neglect Africa, but the continent is innovating and needs inclusive, culturally aware approaches to AI.

Artificial Intelligence. African Insight.
A collaborative project supports African research on AI ethics and human rights, addressing local challenges and opportunities.

The State of AI in Africa
Africa's AI adoption is growing, with significant potential but facing challenges in data access, education, and policy frameworks.

AI Governance in Africa Report 2022
AI shows promise for Africa but also poses risks. Governance is slow, with gaps in legislation and human resources.

AI in Africa Meeting the Opportunity
AI has transformative potential for Africa, promising economic growth and innovation if harnessed responsibly and inclusively.

Africa AI Privacy Report 2025
Examines AI's transformation of Africa's digital landscape across finance, healthcare, law enforcement, education, and governance. Analyzes privacy challenges, regulatory gaps, and offers strategic policy recommendations to balance technological advancement with fundamental rights protection.
